Regular verbs form their past and past participle by adding ed (d). Base Verb Past Past Participle learn learned learned study studied studied cook cooked cooked solve solved solved ask asked asked watch watched watched listen listened listened Irregular verbs do not have definite rules, but there are a few …
Read More »Perfect Progressive Tense
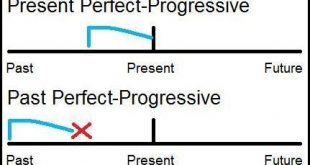
The perfect progressive tense describes actions that repeated over a period of time in the past, are continuing in the present, and/or will continue in the future. The present perfect progressive tense tells you about a continuous action that was initiated in the past and finished at some point in …
Read More »Progressive and Perfect Tense
Progressive Tense The progressive tense involves action that is, was, or will be in progress at a certain time. In the progressive tense, verbs are formed with a “be” verb + ing. run I am running a marathon right now. (present progressive) I was running a marathon at this time …
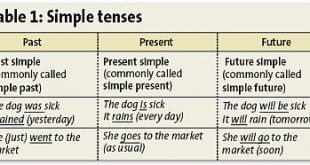
Read More »Simple Tense
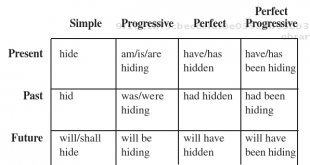
Verb tense tells you when the action happens. There are three main verb tenses: present, past, and future. Each main tense is divided into simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive tenses. Present Past Future Simple finish finished will finish Progressive am/is/are finishing was/were finishing will be finishing Perfect have/has finished …
Read More »Adverbs
Adverbs modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells more about a verb in the sentence. The fire engine runs fast. Listen to his speech carefully. I browse the web frequently. It rained hard. An adverb describes more about an adjective in the sentence. The news is …
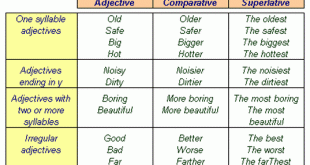
Read More »Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives compare two things. Superlative adjectives compare more than two things Commonly, adjectives that contain only one syllable or end in ‘y’ use ‘er’ to form comparatives and ‘est’ to form superlatives. For adjectives ending in y, change the ‘y’ to ‘i’ before adding the ‘er’ or ‘est’. old …
Read More »Action Verbs
Action verbs express action and are the most common verbs. Action verbs need s at the end with third-person, singular subjects. He eats bread. She walks to the station. It floats on the sea. Negative sentences need do not, does not, or did not. I do not eat bread. He …
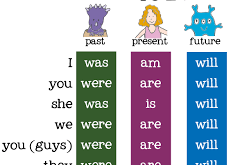
Read More »‘Be’ Verbs
A verb shows action or a state of being. I go home. Home is my place to rest. I like the smell of my house. I feel totally relaxed. Home refreshes me. At home, I get ready for a new day. “Be” verbs indicate a state of being. Verbs must …
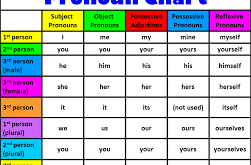
Read More »Pronouns
A pronoun takes the place of a noun. Example story: Mary is one of the heads of the ToJi Corporation. Mary works with Mr. James and Mr. James’ son Tom. Mr. James and Mr. James’ son Tom are experts in biochemistry. Mary, Mr. James, and Tom researched and invented a …
Read More »Possessive Nouns
Possessive nouns are used to indicate ownership. Possessive nouns usually are formed by adding an apostrophe (‘) and s. John’s book Kerry’s car Grandma’s mirror When a noun is plural and ends in s, just add an apostrophe (‘). The kids’ toys My parents’ house The teachers’ lounge If two …
Read More »